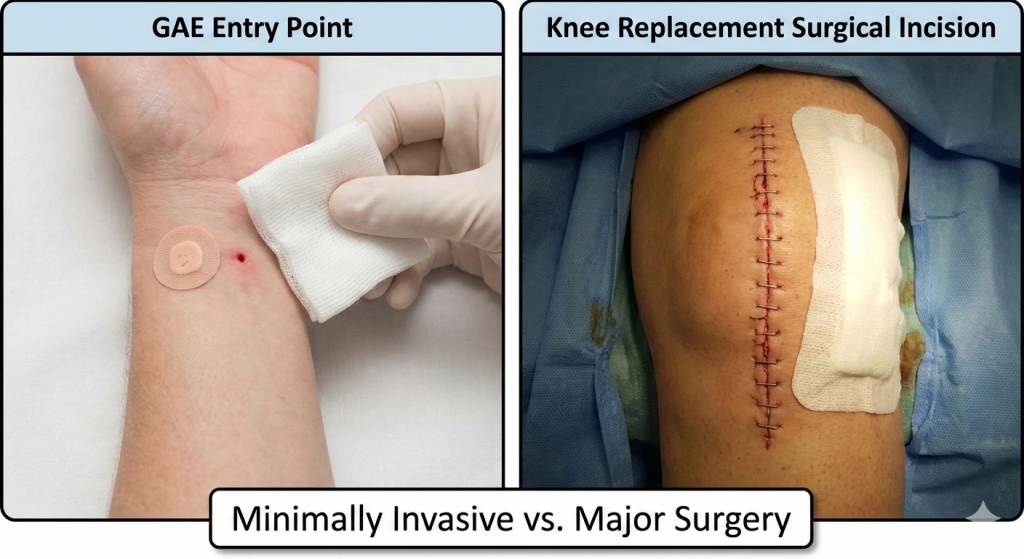
Knee pain can significantly affect your quality of life, making everyday activities like walking the dog or climbing stairs challenging. For many, the pain becomes so severe that medical intervention is the only way to regain mobility.
While knee replacement surgery has long been the standard, newer minimally invasive procedures, such as Genicular Artery Embolization (GAE), are emerging as highly effective alternatives. This article explores the differences between GAE vs. knee replacement surgery to help you decide which path is right for your health and lifestyle.
Understanding Knee Pain and Its Impact
Knee pain can occur from various causes, including arthritis, injury, or general wear and tear. Regardless of the cause, the pain can be debilitating, affecting mobility and overall lifestyle.
Many patients struggle with the decision to seek treatment, especially when traditional methods like physical therapy or cortisone injections no longer provide relief. This often leads to the “treatment gap”, where they are in too much pain for over-the-counter meds, but aren’t ready for a major operation. This is an opportunity to explore joint pain treatment alternatives
See Our Locations for A Consult Near You
What is Knee Replacement Surgery?
Knee replacement surgery, or arthroplasty, involves removing the damaged cartilage and bone of the knee joint and replacing them with artificial metal and plastic components. This procedure aims to solve a mechanical issue by providing a new, smooth surface for the joint to glide on.
How Knee Replacement Works
- Pre-Surgery Preparation: Patients undergo an orthopedic assessment, which includes physical exams and imaging (X-rays/MRIs) to map the joint damage.
- The Procedure: An orthopedic surgeon makes a large incision, resurfaces the bone, and cements the implants in place. This requires general anesthesia and a hospital stay.
- The Recovery Reality: Total knee replacement is often more painful than other joint surgeries (like hip replacement) because the knee is closer to the surface and surrounded by complex ligaments. Regaining a range of motion requires diligent rehabilitation after surgery for three to six months.
How Genicular Artery Embolization (GAE) Works
GAE is a nonsurgical knee pain treatment that takes an entirely non-surgical approach. Instead of fixing a mechanical bone issue, GAE fixes a biological/chemical issue: chronic inflammation.
GAE Procedure Details
GAE targets the growth of new, tiny blood vessels and nerves within the synovium (the lining of the knee joint). When a joint is arthritic, it grows these “junk” vessels that fuel inflammation and transmit pain signals.
- The “Starvation” Method: By strategically blocking these specific genicular arteries with microscopic particles, the procedure essentially starves the inflammation that causes deep, “throbbing” knee pain.
- The Procedure: A specialist inserts a tiny catheter through a pinprick (usually in the wrist or groin). Using real-time imaging, they navigate to the knee and release the particles.
- The Recovery: Because there is no cutting of bone or muscle, recovery is measured in days, not months. Most patients return to regular activities within 48 to 72 hours.
Comparing GAE and Knee Replacement: The “Band-Aid” vs. “The Rehab”
A key factor when weighing the pros and cons of genicular artery embolization (GAE) versus total knee replacement is the surgical risk and expected recovery time.
| Feature | Knee Replacement Surgery | Genicular Artery Embolization (GAE) |
| Approach | Mechanical (Replaces the joint) | Biological (Stop inflammation) |
| Incision | A large surgical incision requires stitches | Tiny pinprick; no stitches |
| Anesthesia | General (Fully asleep) | Local or moderate sedation |
| Recovery Time | 3–12 months for full recovery | 2–5 days for full recovery |
| Pain Level | High; requires intensive PT | Low; “Band-Aid” recovery |
Why Knee Replacement is Challenging
Knee replacement is often painful because the knee joint is closer to the surface and involves more surrounding muscles and ligaments, leading to greater post-operative soreness, swelling, and tightness. Also, regaining one’s range of motion (bending) and overcoming stiffness requires very diligent, sometimes painful, physical therapy.
- Gravity: As a lower joint, the knee swells more post-surgery, which can increase discomfort.
- Stiffness: Overcoming post-operative tightness requires a massive commitment to rehabilitation.
- Hospitalization: This is a significant surgery that typically requires a multi-day hospital stay.
Yet for some patients, knee replacement can offer a permanent solution for severe joint damage. While many patients experience pain relief and improved mobility, knee replacement is generally reserved for severe cases, particularly those with advanced arthritis or joint degeneration.
Another point to discuss with one’s doctor is how long the replacement knee will last. While about 90% of total knee replacements function well for 15-20 years, lifespan varies with patient factors such as activity level, weight, age, and implant quality, and components may loosen or wear out, potentially requiring revision surgery sooner.
Who is the Ideal Candidate for GAE?
Not everyone with knee pain needs a replacement. GAE is often the perfect “middle ground” for patients who:
- Have moderate-to-severe pain due to osteoarthritis.
- They are not yet ready—or are too young—for a total knee replacement.
- Have “failed” other treatments like injections or physical therapy.
- Want to avoid the risks associated with general anesthesia or major surgery.
- Have “bone-on-bone” pain, but the primary symptom is inflammation and throbbing.
A benefit of GAE is that, because it’s minimally invasive, it involves less trauma to the body, reducing recovery time. Most patients can resume daily activities soon after the procedure. Additionally, as a less invasive option, GAE carries lower risks and complications.
Moving Forward On Your Path to Pain-Free Mobility
Choosing between GAE and knee replacement surgery is a personal decision based on the severity of your condition and your recovery goals. If you are looking for a permanent mechanical fix and are willing to undergo extensive rehab, surgery may be the answer. However, if you want to break the cycle of inflammation and get back to your life in days, GAE offers a revolutionary path forward.
A diagnosis is the first step toward walking without pain again. Consult a vascular specialist to determine whether “starving” your knee pain is the right move for you.
Choosing between GAE and knee replacement depends on several factors, including the severity of the knee condition, overall health, and personal preferences. Consulting with a healthcare professional can provide guidance tailored to individual needs.
Why Choose USA Pain Center?
Understanding advanced arthritis and exploring treatments like Genicular Artery Embolization can help you make informed decisions about managing pain and maintaining mobility. A personalized evaluation can clarify which options align best with your goals and lifestyle.
Our staff is a highly experienced team of interventional radiologists who can evaluate and treat knee pain across an extensive network. We are poised to offer the most technically advanced treatments to help patients resolve pain with minimally invasive solutions that restore their mobility and quality of life.
Frequently Asked Questions: GAE vs. Knee Replacement
Is Genicular Artery Embolization (GAE) covered by insurance?
Yes. In most cases, GAE is covered by Medicare and many private insurance plans when it is deemed medically necessary for treating chronic knee pain caused by osteoarthritis. Our team at USA Pain Centers can help you verify your specific coverage during your initial consultation.
If I have GAE now, can I still have a knee replacement surgery later?
Absolutely. One of the most significant benefits of GAE is that it does not alter the anatomy of the knee joint or the bone. It targets the blood vessels and nerves in the soft tissue (synovium). If your arthritis progresses years down the line and you decide surgery is necessary, your orthopedic surgeon will still have all the same options available.
How long does the pain relief from GAE last?
Clinical studies show that most patients experience significant pain relief for 6 months to several years. While a knee replacement is considered a “permanent” mechanical fix, GAE is a highly effective way to manage the biological pain of arthritis without the risks of major surgery.
Is the GAE procedure painful?
No. Most patients feel only a slight “pressure” or a pinprick sensation at the entry site (wrist or groin). Unlike surgery, which requires general anesthesia, GAE is performed under local anesthesia and “twilight” sedation. You remain comfortable and relaxed throughout the 45- to 60-minute procedure.
What are the particles used in GAE made of?
The particles are microscopic, biocompatible spheres (often made of a synthetic polymer). They are designed to remain permanently in the specific tiny vessels to prevent regrowth and further inflammation. They are safe, inert, and not felt once in place.
Can GAE treat “bone-on-bone” arthritis?
Yes. Even in serious “bone-on-bone” cases, much of the actual pain is caused by the inflamed lining of the knee (synovitis) rather than the bone itself. By shutting off blood flow to the inflamed lining, GAE can significantly reduce pain, even when cartilage is thin.