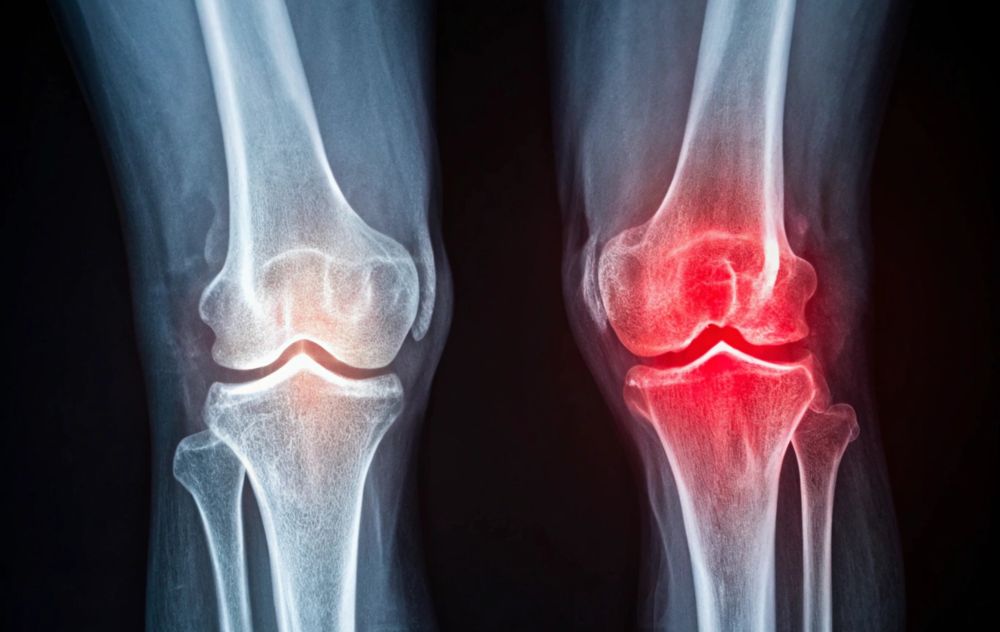
Knee pain affects millions of people every year, often making simple tasks—like walking, climbing stairs, or standing up—feel unbearable. While injuries can cause short-term discomfort, chronic inflammation is one of the leading causes of long-lasting knee pain and joint damage.
What Is Chronic Inflammation?
Inflammation is your body’s natural defense mechanism against injury or infection. When something goes wrong, your immune system releases chemicals that increase blood flow and white blood cell activity to heal the area.
In acute inflammation—such as after a sprain—this response is temporary and beneficial.
But in chronic inflammation, the process doesn’t shut off. The body continues to send inflammatory signals long after they’re needed, creating a cycle of swelling, pain, and tissue damage.
Over time, this ongoing inflammation in the knee can lead to degenerative joint disease, or osteoarthritis, which breaks down cartilage and limits movement.
How Inflammation Damages the Knee Joint
The knee is one of the most complex and frequently used joints in your body. It’s made up of bones, cartilage, ligaments, tendons, and the synovial membrane that produces lubricating fluid.
When inflammation becomes chronic, several harmful changes occur:
-
Cartilage Breakdown
Inflammatory enzymes gradually erode the smooth cartilage that cushions the joint. Without this protective layer, bones begin to rub against each other—causing stiffness, pain, and grinding sensations. -
Synovial Thickening
The synovial lining that produces joint fluid can become thickened and overactive, leading to swelling and pressure inside the knee. -
Bone Spurs and Structural Changes
The body tries to protect the damaged joint by forming new bone growths called osteophytes, or bone spurs. These can restrict mobility and further aggravate inflammation. -
Reduced Blood Flow
Chronic inflammation disrupts normal blood circulation within the knee’s small arteries, preventing oxygen and nutrients from reaching healing tissues.
These changes create a vicious cycle: inflammation damages the joint, and joint damage triggers more inflammation.
Common Signs of Chronic Knee Inflammation
If your knee pain persists for more than a few weeks or worsens over time, it could be due to chronic inflammation. Watch for these key warning signs:
-
Persistent pain and stiffness, especially in the morning
-
Swelling or warmth around the joint
-
Cracking or grinding sensations (crepitus)
-
Limited range of motion
-
Pain that worsens after activity or prolonged sitting
Ignoring these symptoms can lead to progressive joint damage and reduced mobility.
What Causes Chronic Inflammation in the Knee?
Several underlying conditions can trigger or worsen inflammation:
-
Osteoarthritis (wear-and-tear arthritis)
-
Rheumatoid arthritis (autoimmune joint inflammation)
-
Overuse or repetitive motion injuries
-
Obesity (extra weight increases pressure and inflammatory cytokines)
-
Poor circulation or vascular issues
Lifestyle factors—such as a sedentary routine, poor diet, and lack of joint support—can also accelerate inflammatory damage.
Protecting Your Knees from Long-Term Damage
Reducing inflammation isn’t just about treating pain—it’s about preserving your joint health. Here are a few steps you can take to support recovery and prevent further damage:
-
Maintain a healthy weight to reduce joint pressure
-
Stay active with low-impact exercises (swimming, cycling, yoga)
-
Follow an anti-inflammatory diet rich in omega-3s, fruits, and vegetables
-
Avoid prolonged sitting or standing when possible
-
Work with your pain specialist to develop a long-term management plan
How Genicular Artery Embolization (GAE) Targets Inflammation
Traditional treatments like pain medication, steroid injections, or physical therapy often provide only temporary relief because they don’t address the root cause: excess blood flow fueling inflammation in the knee.
Genicular Artery Embolization (GAE) is a minimally invasive, non-surgical procedure that works differently. Using advanced imaging, an interventional radiologist identifies the small arteries (genicular arteries) feeding the inflamed tissue. Tiny particles are then injected to reduce this abnormal blood flow, easing inflammation and pain.
By treating the source of inflammation, GAE can:
-
Relieve pain and stiffness
-
Improve mobility and function
-
Reduce swelling
-
Slow or prevent further joint damage
Clinical studies have shown that GAE provides long-lasting relief—often for several years—without the need for invasive knee replacement surgery.
When to See a Knee Pain Specialist
If you’ve been living with knee pain that won’t go away—or you’ve tried multiple treatments without relief—it may be time to consider GAE. At USA Pain Center, our specialists use advanced, image-guided techniques to treat inflammation directly and help patients regain mobility, comfort, and confidence.
Meet the Experts at USA Pain Center
Chronic inflammation is more than just discomfort—it’s a signal that your body needs attention. Don’t let knee pain control your life. Schedule a consultation with USA Pain Center today and learn how Genicular Artery Embolization can provide lasting relief without surgery or long recovery times.
📍 Find a USA Pain Center near you and start your journey toward pain-free movement.